The Majority of White Blood Cells in Circulation Include
These are powerful white blood cells that destroy bacteria and fungi. These include platelet-derived growth factor PDGF 14 and fibroblast growth factor FGF.

18 4 Leukocytes And Platelets Anatomy Physiology
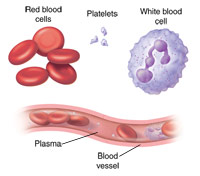
The different components that make up blood.

. These cells have a single nucleus with multiple lobes. White blood cells WBCs include lymphocytes the cornerstone of the immune system and myeloid cells which. White blood cells WBCs include lymphocytes.
Consist of T cells natural killer cells and B cells to protect against viral infections and produce. Neutrophils are white blood cells that are classified as granulocytes. They are phagocytic and have chemical-containing granules that destroy pathogens.
6048 The survival of white blood cells as living cells depends on their continuous production of energy. They are chemically drawn to bacteria by cytokines and migrate through tissue toward infection sites. The cells responsible for the production of circulating antibodies are the.
White blood cells WBC are a heterogeneous group of nucleated cells that can be found in circulation for at least a period of their life. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. The majority of white blood cells in circulation include-neutrophils and lymphocytes-eosinophils and basophils-macrophages-erythrocytes.
T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells found in the. Low blood cell counts in any of these three cell lines red cells white cells or platelets are the hallmark feature of MDS. Neutrophils are medium-sized white blood cells with irregular nuclei and many granules that perform various functions within the cell.
They defend against bacterial or fungal infection. Lymphocytes are responsible for the specific defence response to infection known as immunity. Circulatory and pulmonary systems.
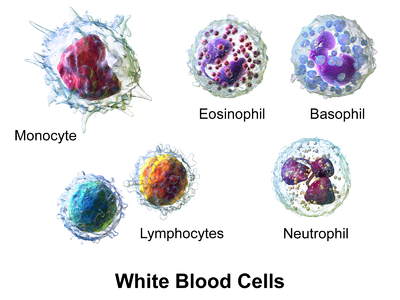
Neutrophils possess a single nucleus that appears to have multiple lobes. The different types of white blood cells leukocytes include neutrophils basophils eosinophils lymphocytes monocytes and macrophages. Plasma is 90 water and is beige in color.
Learning Objectives Distinguish between the two major types of leukocytes white blood cells. Leukocytosis is characterized by an elevated number of white blood cells leukocytes in the blood circulation. Red cells flow in the blood circulation to transport oxygen.
These substances are carried to and from the cells by the plasma. Monocytes are while blood cells WBCs that are originated from the bone marrow and circulates through the blood for 1-3 days. Lymphocytes account for 2030 of circulating white blood cells but actually spend very little time in the circulation.
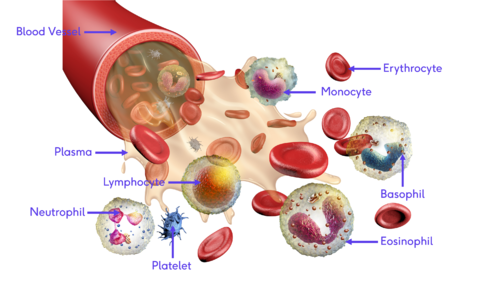
Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell in the body with levels of between 2000 to 7500 cells per mm 3 in the bloodstream. The lungs and pulmonary system. Plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets.
There are five types of white blood cells. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor TCR on their cell surface. Every cell needs access to the circulatory system in order to function since oxygen is essential for proper cell function.
Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cell constituting 60-70 of the circulating leukocytes. They are chemically drawn to bacteria and migrate through tissue toward infection sites. Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cell in circulation.
B eosinophils and basophils. Candler BallardCenters for Disease Control and Prevention CDC Image Number. Red blood cells white blood cells and platelets.
Neutrophils are phagocytic meaning that they engulf and destroy target cells. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Plasma contains digested food chemicals and waste products. Their activity and death in large numbers form pus. Question 20 1 point Saved There are tests available to allow us to differentiate B cells from T cells and their subtypes.
The majority of RBCs platelets and most of the WBCs are formed in the red marrow while. Then they migrate to tissues to differentiate into tissue resident macrophages or dendritic cells. They play a most important role in phagocytosis and immunity and therefore in defense against infection.
Phagocytose engulf and then digest cellular debris stimulate lymphocytes DENDRITIC CELLS. Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cell in circulation. Circulatory system and the heart.
Destroy invaders and signal to others for help MACROPHAGES. GRANULOCYTESwhite blood cell filled with microscopic granule sacs containing enzymesdigest microorganisms innate nonspecific T-LYMPHOCYTES. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response.
These cells are the most abundant granulocyte in blood circulation. The majority of white blood cells in circulation include A. They are usually first responders to microbial infection.
The majority of white blood cells in circulation include A neutrophils and lymphocytes. 16 Blood cell adhesion to the vascular endothelium can be mediated via the platelet the WBC or the endothelial cell with changes. Saved The majority of white blood cells in circulation include Question 19 options.
Help protect your body from infections by killing bacteria fungi and foreign debris. 15 These growth factors are strongly linked to the smooth muscle cell proliferation underlying most cases of restenosis. The majority of RBCs platelets and most of the WBCs are formed in the red marrow.
Their normal concentration in blood varies between 4000 and 10000 per microliter. The three kinds of blood cells that make up the solid part of blood are.

Blood And Blood Vessels Healthdirect
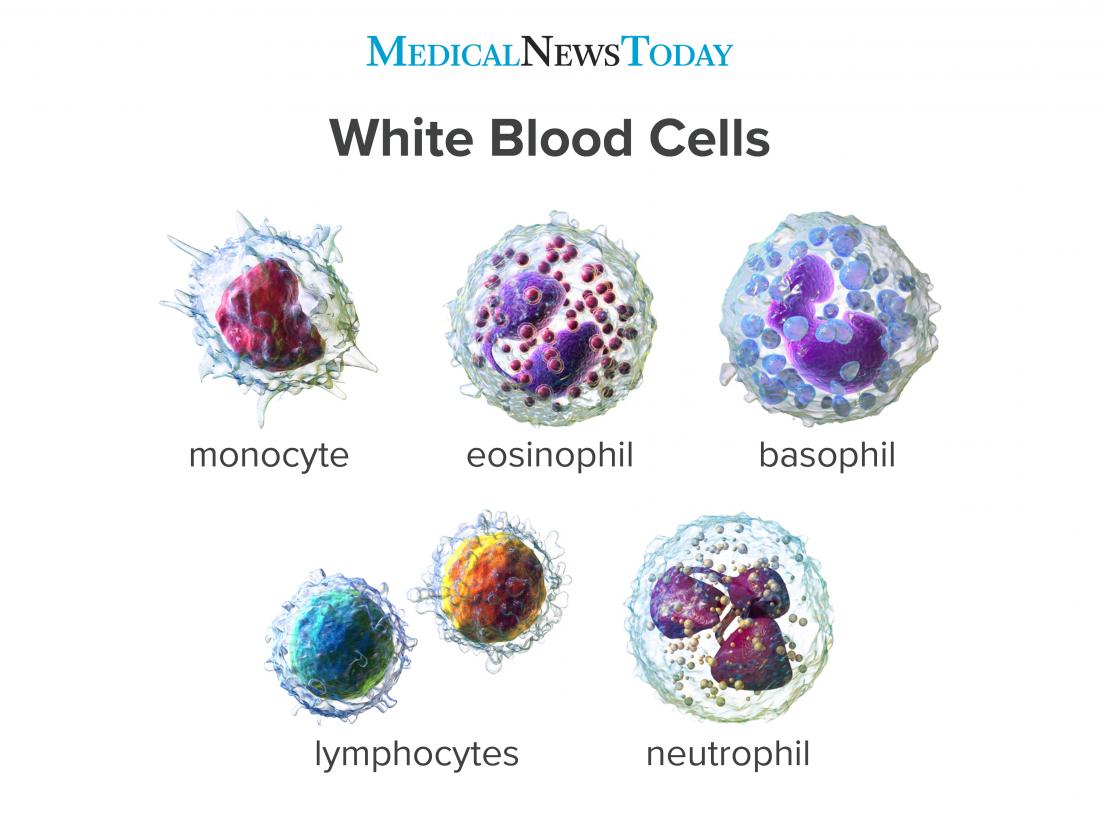
Complete Blood Count Definition Purpose Results And More

Blood Production Of Red Blood Cells Erythropoiesis Britannica
21 2 Components Of The Blood Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
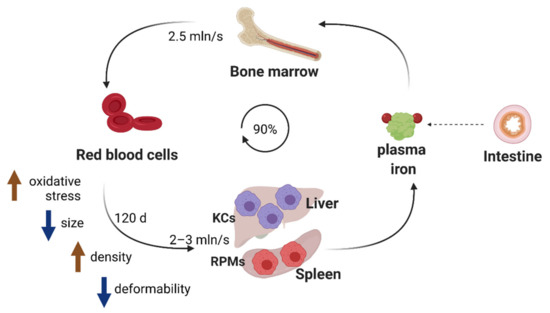
Genes Free Full Text The Multiple Facets Of Iron Recycling Html

Red Pulp An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lymphatic System Facts Functions Diseases Live Science
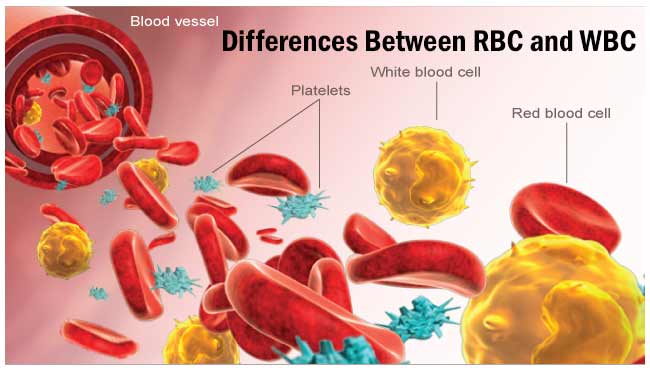
Differences Between Red Blood Cells Rbc And White Blood Cells Wbc
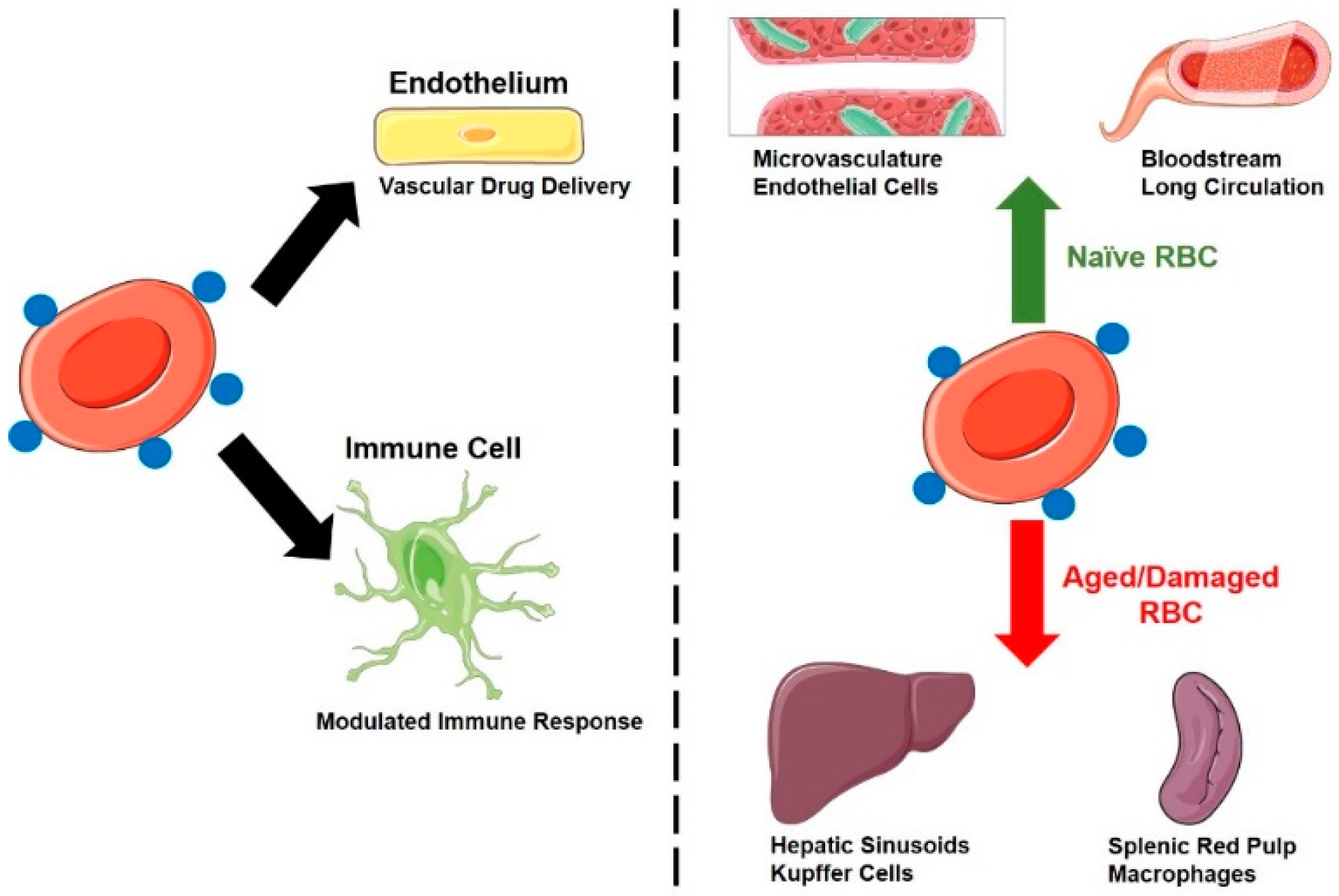
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Vascular Drug Delivery Using Carrier Red Blood Cells Focus On Rbc Surface Loading And Pharmacokinetics Html

Leukocytes And Platelets Anatomy And Physiology Ii
21 2 Components Of The Blood Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Comments
Post a Comment